Connecting three cameras to an industrial Raspberry Pi allows for more multifaceted image analysis. For example, when used for product inspection or abnormality detection on a production line, three viewpoints instead of one would improve accuracy.
The same is true for object and human body detection, skeletal pose estimation, etc. Monitoring from different angles has the advantage of expanding the range of detection.
When we hear the words AI image processing and edge processing, we tend to imagine a large system, but in fact, Raspberry Pi is used in systems that are practical enough.
PiLink Co., Ltd, which handles Raspberry Pi for industrial use, sells the Raspberry Pi ComputeModule 5 („CM5“) in a rugged enclosure case suitable for on-site environments.
For testing purposes, we put Halito-8L on a Raspberry Pi 5 (hereafter referred to as Pi 5) instead of CM5 and ran each of the three USB cameras using the sample AI models in the installed AI framework.
AI image processing also on Raspberry Pi
When one imagines using Raspberry Pi for AI, it is often thought that it would be impossible with inexpensive boards and non-powerful performance. It is true that it is numerically inferior to a typical PC or server. However, it is practical enough when using AI accelerator routers.
If you are wondering whether a typical small Windows PC is sufficient for performance alone, this is not really the case. This is because there are many other benefits that are important in factories and other applications.
AI processing, which was difficult with the previous Raspberry Pi due to its lack of performance, is also being utilized with the performance of the CM5, which is the latest at the time of writing, and its rich connection interfaces.
The Raspberry Pi has been well received in industrial applications because it seems to „compensate for hardware weaknesses with a chassis and design that maximizes operating cost efficiency and program flexibility.“
Testing

On a Pi 5 with Hailo connected, we installed the AI framework and ran the sample AI model.
Environment used:
- Raspberry Pi 5 MEM8GB
- Raspberry Pi OS (bookworm)
- Hailo-8L
- Using sample AI frameworks and AI models
- Three 4K-ready 8-megapixel USB cameras
- microSD card activation
The main types of AI frameworks and AI models are
It calls the framework, which is the execution environment, and loads the learned models.
- AI frameworks (TensorFlow, PyTorch, ONNX Runtime, etc.)
- AI models (YOLOv5 (object detection), MobileNet (classification), PoseNet (posture estimation), etc.)
Please see the desktop capture image we tested this time.
The OS was running on a microSD card, but the speed was generous. There is zero frame drop.
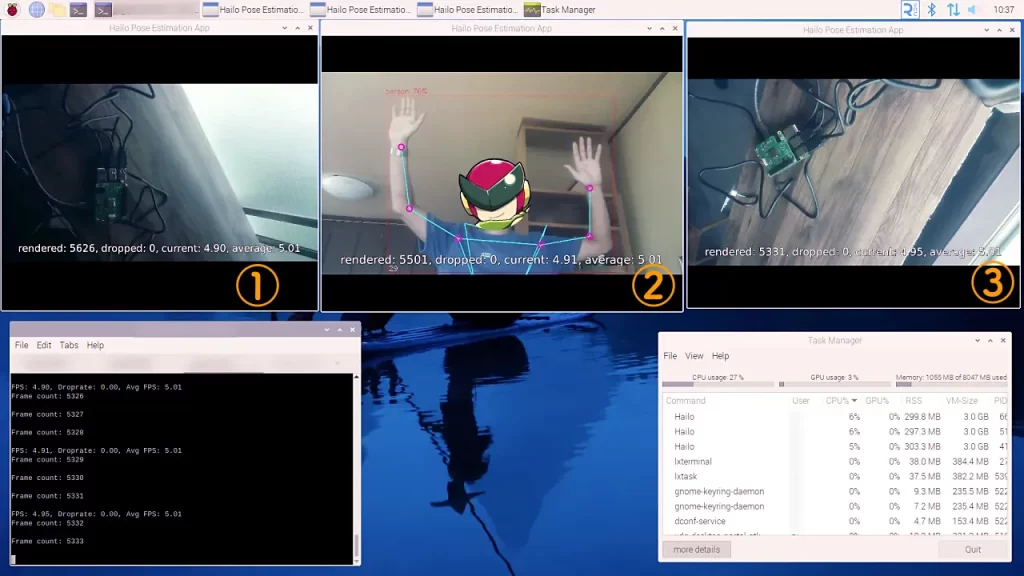
Windows (1) through (3) show the images from the respective USB cameras.
You can see the terminal in the lower left corner, with three tabs open to run the AI model.
In the lower right corner you can see the TaskManager that is included in the Raspberry Pi OS to see the utilization. As you can see, the CPU is at 27% and the memory used is only about 1GB.
There are three Hailo tasks, CPU usage is 6%, 6%, and 5%, and the Raspberry Pi itself has only a small amount of CPU usage.
The AI model is running object detection and posture estimation, respectively. Since there is only one human model (②), ① and ③ are images of the Raspberry Pi being executed from different angles.
You can see that (2) is working well with the posture estimation point markers and lines displayed.
By the way, you are recognized at 70% as a person.
If you do not move too violently, the posture estimation will respond and draw properly.
The monitor I am displaying is HDMI output from a Pi 5 and is full HD (1920×1080).
The USB camera can handle up to 4K if the frame rate is reduced. This time I put three smaller 800×600 windows side by side at 30fps.

Even the Pi 5 for hobby use is felt to be adequate with Hailo.
High degree of freedom and low cost of development
It can adopt an OS with no extras, and open source software (OSS) allows native use of each library and application. The necessary customization is better suited than a standard PC, whether it is to work with proprietary programs or to function as a server.
The device also has an HDMI port, so it can be handled like a standard PC, such as displaying on a monitor, and has a high degree of flexibility.
Program development can also be reduced in cost and speed by using already existing AI frameworks and AI models.
Compact, power-saving and low cost
Raspberry Pi has the advantage of being small and lightweight, consuming less power, and having low running costs due to long hours of operation.
Since the main unit is inexpensive for commercial use, initial costs can be kept low, and it is a good idea to introduce the system on a trial basis to see how it fares.
Robust hardware
The main unit of Raspberry Pi is a bare board. To actually use the Raspberry Pi, you will need to put it in one of the cases.
The industrial Raspberry Pi „PL-R5“ is designed for rather harsh environments, with a housing that can withstand high temperatures, vibration, and shock, and strong connectors.
Hailo + LTE
Some models for AI image processing are available with Hailo on board and LTE implemented at the same time. They can be housed together with the Raspberry Pi in a robust case, so you only need the same one unit.
LTE makes it convenient to send the acquired data to the cloud for storage or remote control, without being aware of LAN cables or Wi-Fi signals.
AI-related terminology
Although not limited to AI, a variety of technical terms are used wildly in computers. This is an area where Japanese are not good at because most of the words are from English-speaking countries. English is expressed as it is in katakana Japanese or translated Japanese.
Some terms have many similar expressions, so it is easier to understand if you first know what they stand for.
Let me lay out some terms as examples.
Hailo module (AI accelerator)
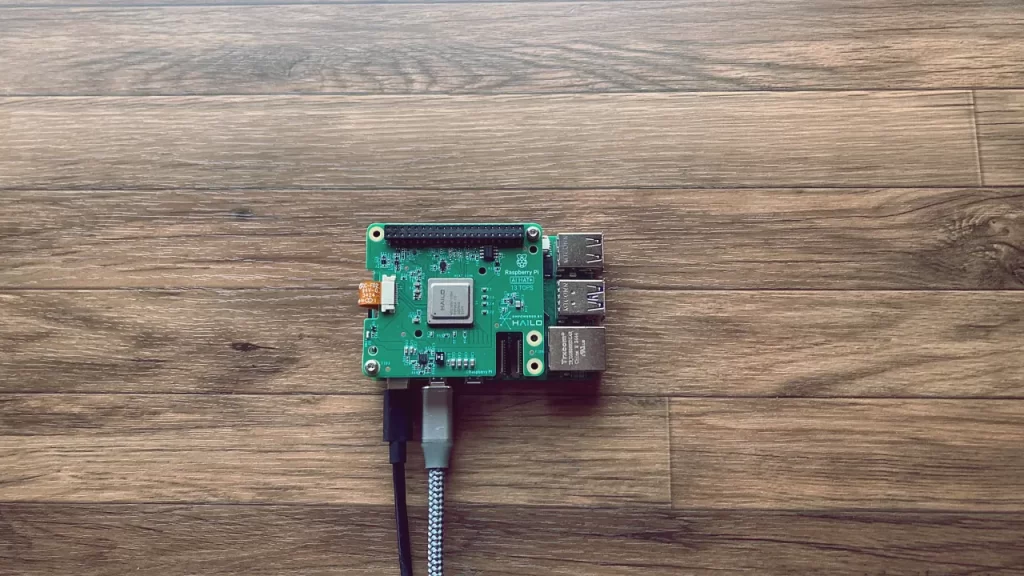

The Raspberry Pi CM5 and Pi 5 can work with a module with a dedicated AI chip called Hailo.
Hailo is a chip developed by an Israeli company. The semiconductors in the device are made so that even small devices can perform AI processing, such as image recognition, at high speed.
Like the Raspberry Pi, it is small and has low power consumption, making it a dedicated AI chip for embedded applications. This allows AI models to be handled even on the Raspberry Pi, which is less powerful than a typical CPU and has an Arm architecture.
The Hailo-8L we used is an M.2 form factor AI inference accelerator; because it is an M.2 form factor, it can be easily installed in a CM5/Pi 5 as well as an SSD drive of the same standard.
Hailo is the company and product name of Hailo Technologies, Inc.
edge inference
Edge here means „edge“ (hashi) in English.
In the computer industry, it is used to refer to a „field“ such as a production site.
What is the edge from what? It refers to the devices (terminals) in the field that are at the edge from the perspective of the servers in the cloud. The expression „edge device“ is exactly what it means.
When inference (≈decision making) using AI models is performed by a device installed onsite, it is described as „edge inference“. It refers to a system in which decisions are processed by a computer on-site, rather than waiting for a response from a server (cloud) on the Internet.
The advantages of edge inference are that, unlike processing on the cloud side, there is less latency due to the network, and data leakage off-site is reduced from a security and privacy perspective.
neural network
Neural networks are technical models (neural networks) that embody brain nerve cells „neurons“.
Deep Learning“ is a term that is already familiar to us. In Japanese, it is „deep learning“ and refers to a system that learns features from a large amount of data.
Artificial intelligence (AI) uses neural networks to perform machine learning or deep learning.
Machine learning“ refers to a technology in which a computer learns from data and automatically makes decisions, and „deep learning“ is a technology in which multiple layers are used to increase accuracy.
Hailo-8L is a chip that can perform mainly deep learning at high speed.
AI Image Processing
When we say „AI processing,“ we mean a very broad term.
In the case of processing images captured by a camera, such as in this test, the term „AI image processing“ can be used.
AI image processing runs deep learning algorithms. It uses multi-layered machine learning from large amounts of data to infer results.
Images and videos are analyzed, and differences between people, objects, and specific movements are discerned, processed, and judged.
Specifically, they are used to recognize human faces, distinguish between cats and dogs, and detect normal and abnormal conditions in products.
We see this expressed in the common phrase rephrased as „AI thinks, learns, and makes decisions“.
Raspberry Pi is also a candidate for AI image processing system
Nowadays, image recognition systems are being introduced for various industrial applications. If there is a system that can be built at low cost, there are many companies that would love to introduce it.
If you are considering implementing AI image processing, we felt that a Raspberry Pi with Hailo would be a perfect fit.
Besides the low cost advantage, the Raspberry Pi is a small device to begin with. Even when housed in a robust case, it is still very small for commercial use.
The actual situation on site varies, but not having to worry about where to install it will surely be helpful.
A system using Raspberry Pi and AI image processing is nothing extensive and can be implemented for product inspection and safety monitoring.
Because it is an edge device, real-time processing can be performed on site.
Once the data is accumulated and trained, the company can improve efficiency with its own AI processing.
Even a single Raspberry Pi 5, as in this test, has enough performance to handle multiple cameras simultaneously.
Now that it is difficult to secure skilled craftsmen, it may be urgent to introduce a system that can be utilized by something other than the human eye.
Article contributed by Raspida
Raspberry Pi information site that even non-engineers can enjoy using raspida.com a Raspberry Pi information site that even non-engineers can enjoy and handle. He also contributes technical blog articles to the PiLink site on the Raspberry Pi for industrial use.


